Yarn vs. Npm In 2020
Table Of Contents
In the JavaScript world, people share millions of pieces of code to avoid spending time on some necessary functionality, that is already done by others.
Shared code, in turn, may depend on another part of the shared code, and so on.
All these dependencies are managed by package managers, whose main function is to install some code from a global registry into an engineer's local environment.
Both yarn and npm, are package managers for JavaScript applications.
Npm
Npm is a default package manager for Node.js runtime environment.
It was written in JavaScript and initially released in January 2010 by Isaac Z. as a result of having "seen module packaging done terribly" and with inspiration from other similar projects such as PEAR (PHP) and CPAN (Perl).
It consists of the command line client and an online database with private and public packages, the so-called npm registry.
This registry is accessed via the client, and all available packages can be browsed via the npm website:
The package manager belongs to npm, Inc. which was acquired by Github in March 2020.
Install Npm
Npm is automatically installed with Node.js.
There are a few ways to install it on your system:
-
Using nvm (Node Version Manager) -> the recommended approach
The full guide can be found here.
-
Using Node installer -> may result i npermission errors
Download and install Node.js from here.
To verify the installation, run the following commands:
node -v
And
npm -v
If they work and print the installed version, everything is fine:

Yarn
Yarn is a package manager that was developed by Facebook as an alternative to npm and released in 2016.
Do not consider this tool as a replacement for npm because it relies on the modules from the npm registry (you use it to install the dependencies hosted on the npm, right?).
Think of it as a new installer that relies on the same npm structure with a different installation method.
It was developed when the team of Facebook developers faced some npm limitations.
Many of our projects at Facebook, like React, depend on code in the npm registry. However, as we scaled internally, we faced problems with consistency when installing dependencies across different machines and users, the amount of time it took to pull dependencies in, and had some security concerns with the way the npm client executes code from some of those dependencies automatically. We attempted to build solutions around these issues, but they often raised new issues themselves...
Read more about the reasons for creating yarn here.
Install Yarn
Yarn offers great documentation that describes a lot of ways to install it on your machine.
Verify the installed version:

Latest Versions Comparison
According to these benchmarks, the latest versions of npm and yarn do not differ significantly in speed.
In general, yarn tends to be slightly faster in the most popular use cases.
But if performance is really important to you - consider using pnpm instead.
The Differences
Installation
Npm is installed automatically with Node.js, yarn must be installed manually.
Saving installed dependencies
Npm does not save added dependencies by default (--save/--save-dev flag must be added), yarn does.
Popularity
Npm has 17.2K stars on Github, yarn has 39K (at the time of writing this article).
Performance
The latest yarn version is a little faster than the latest npm for most cases.
In the past, yarn was much, much faster until the npm version 5.0 came out, which claims to be 5x times faster than its previous versions.
Security
Yarn offers more security because npm automatically executes a code that allows other packages to be included in the fly.
Yarn installs those files that are only taken from the yarn.lock or package.json files.
Lock files
Npm generates package-lock.json, yarn generates yarn-lock.json.
The purpose of the lock file is to lock down the versions of the installed dependencies, specified in the package.json file.
Each time a dependency is added, updated or removed, the lock file is automatically updated.
Global packages installation
Npm uses -g flag to install a package globally, yarn uses the word global.
In a global installation with node, modules are placed in {prefix}/lib/node_modules and executable files are stored in {prefix}/bin, where {prefix} is usually something like /usr/local.
It also installs man pages in {prefix}/share/man if they are included.
A man page (short for manual page) is a form of software documentation usually found on a Unix or Unix-like operating system.
The location for the packages installed globally with yarn: ~/.config/yarn/global.
The local installation for both will install the package into the current working directory.
Node modules end up in ./node_modules, executable files are put in ./node_modules/.bin/, and man pages are not installed at all.
New CLI commands
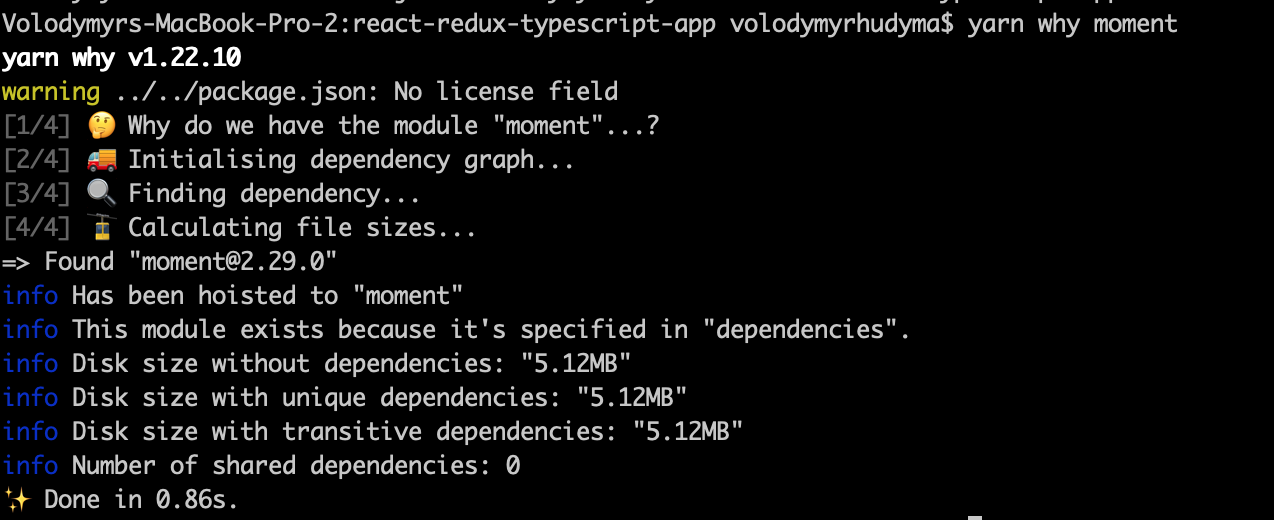
Yarn provides why command which checks why dependency exists in the project.
It also checks which other packages depend on it, or whether it has been explicitly marked as a dependency in the package.json manifest.
The output of yarn why <package>:
Yarn allows you to check the licenses for all installed packages with the yarn licenses list command.
The output of yarn licenses list:
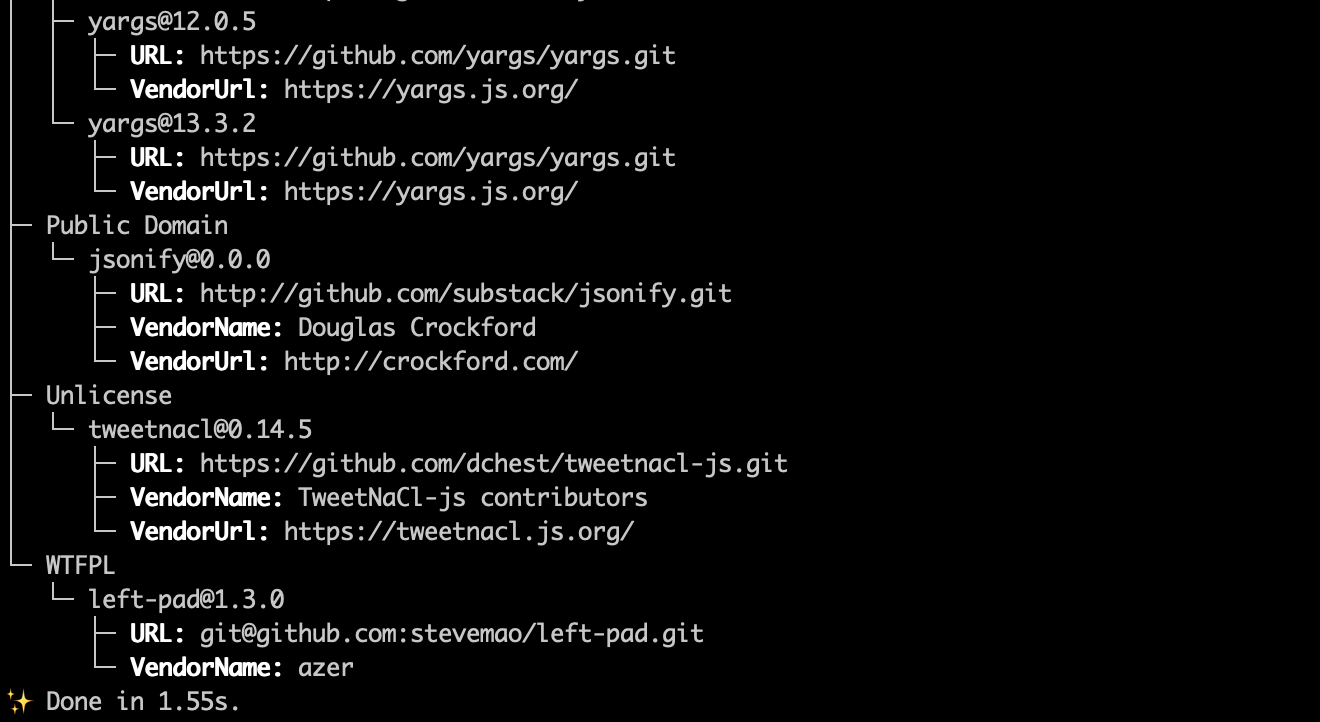
After this command is executed, yarn prints all installed packages in alphabetical order along with the license information.
Caching
Both package managers have a cache, but, according to the benchmarks, yarn cache is faster.
Most Used Commands
After setting up the environment, it is necessary to know some basic commands to get started with these great tools.
Here is a list of the most popular and frequently used commands for both package managers.
Initialize a project
yarn init | npm init
Run tests
yarn test | npm test
Install all dependencies
yarn | npm install
Install dependency
yarn add <package> | npm install <package>
Install dev dependency
yarn add <package> --dev | npm install <package> --save-dev
Install global dependency
yarn global add <package> | npm install <package> --global
Uninstall dependency
yarn remove <package> | npm uninstall <package>
Uninstall dev dependency
yarn remove <package> | npm uninstall <package> --save-dev
Uninstall global dependency
yarn remove <package> global | npm uninstall <package> --global
Update dependencies
yarn upgrade | npm update
Yarn Workspaces
Workspaces are a new way to set up the architecture of the project.
They allow you to organize the code base with a monorepo.
Monorepo (mono repository) is a software development strategy where code for many projects is stored in the same repository.
The idea is to have several isolated packages (projects) in a single repository.
Alternatively, packages can be stored in separate repositories, but this has a negative impact on the developer's experience, code sharing and maintainability.
Imagine having to open 5 pull requests, instead of only one.
There is no alternative for this feature in npm.
To learn more about workspaces, read this article.
Summary
Both tools are great to be used for managing project dependencies.
Yarn brings some improvements, such as more security or slightly higher speed and some new commands, like checking why the given package is installed and printing the licenses for each installed dependency.
That is why I prefer to use it.