How To Validate An Email Address In JavaScript?
Table Of Contents
Web applications should prevent a possibility of entering incorrect data, especially if it is such important information as email address.
Email address validation is a must for all websites, not only to prevent fake data from being sent to the server, but also to improve the overall User Experience.
It is very easy to make an unintentional mistake and wait a few hours for a confirmation email that is never sent to the correct address.
Of course, we can not prevent all mistakes, such as a typo in the email prefix, but we can do our best to make sure the prefix does not contain strange characters and that the format and email domain are correct.
But before we learn how to validate an email address in JavaScript, let us take a quick look at the structure of email addresses and see a few examples of correct and incorrect addresses.
Email Address Structure
Email is a subset of ASCII characters divided in two by the @ symbol.
The first part (email prefix) contains private information, while the second part (email domain) contains the domain name where the email was registered:
<prefix>@<domain>
Both parts have some criteria that must be met for the email address to be considered valid.
Email Prefix Limitations
Email prefix should include:
- Letters and numbers: A-Z, a-z, 0-9
- Special characters: !, #, $, %, &, ', *, +, -, /, =, ?, ^, _, `, {, |
Email Domain Limitations
Email domain consists of a domain name and a top-level domain (.com, .net, .org) and should include:
- Letters and numbers: A-Z, a-z, 0-9
- Hyphen (-) or dot (.)
Example Email Addresses
After learning the rules, we can identify whether an email address is correct or not.
Correct email addresses:
- johndoe@gmail.com
- john-doe@yahoo.com
- john-doe%123%@mailbox.org
Incorrect email addresses:
- johndoegmail.com - doesn't contain @ sign
- johndoe@.com - missing domain name
- johndoe@gmail - missing top-level domain
So, let's start with writing a code that will validate an email address based on the rules above and output an information whether the given email address is correct or not.
Ways To Validate Email Address
It is important to note that we will create a function that only checks if an email address has a correct format.
This function will not check if the given email address exists and if we can deliver messages to it.
There are a few ways to validate an email address in JavaScript:
- Using a Regular Expression
- Using built-in HTML5 email validation
- Using a third-party library
Each of these options has its own advantages and disadvantages, which we will discuss later.
Regular Expression
The most common way to validate an email address in JavaScript is to use a Regular Expression.
Unfortunately, there is no general pattern that can be used to validate 100% of emails.
Each developer has their own saved, found on the Internet.
I typically use the following pattern, which supposedly works for more than 99% of emails:
/^(([^<>()\[\]\\.,;:\s@"]+(\.[^<>()\[\]\\.,;:\s@"]+)*)|(".+"))@((\[[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\])|(([a-zA-Z\-0-9]+\.)+[a-zA-Z]{2,}))$/Note that you don't have to memorise or understand the entire pattern, just save it somewhere for later use.
Let's create a function that uses mentioned pattern:
const isEmailValid = value => {
const pattern = /^(([^<>()\[\]\\.,;:\s@"]+(\.[^<>()\[\]\\.,;:\s@"]+)*)|(".+"))@((\[[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\])|(([a-zA-Z\-0-9]+\.)+[a-zA-Z]{2,}))$/;
return pattern.test(value.toLowerCase());
};The above example checks whether the value passed matches the pattern specified, and returns the boolean result.
Let's test our function:
isEmailValid("johndoe@gmail.com"); // true
isEmailValid("john-doe@yahoo.com"); // true
isEmailValid("john-doe%123%@mailbox.org"); // true
isEmailValid("johndoegmail.com"); // false
isEmailValid("johndoe@.com"); // false
isEmailValid("johndoe@gmail"); // falseIt works as expected for the email addresses mentioned in this article.
Built-In HTML5 Validation
The easiest way to validate an email address in JavaScript is to use built-in HTML5 validation.
All you need to do is use an email as the type of an input field:
<form>
<input type="email" placeholder="Email Address">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>Uses will see a warning message if they try to enter an incorrect email address:
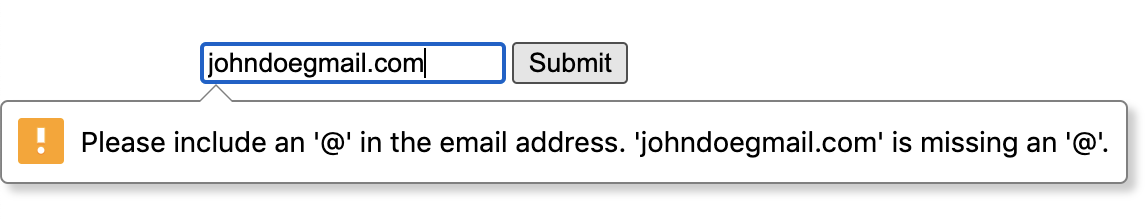
Browsers that support type="email", implement the algorithm corresponding to the following Regular Expression, according to MDN:
/^[a-zA-Z0-9.!#$%&'*+\/=?^_`{|}~-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9](?:[a-zA-Z0-9-]{0,61}[a-zA-Z0-9])?(?:\.[a-zA-Z0-9](?:[a-zA-Z0-9-]{0,61}[a-zA-Z0-9])?)*$/If you need further restrictions on the email address, such as only allowing email from a specific domain, you can use the pattern HTML5 attribute:
<form>
<input type="email" pattern=".+@gmail\.com" placeholder="Email Address">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>Even though the following email: johndoe@yahoo.com is perfectly fine, we get an error message because only gmail.com is allowed:

Third-Party Library
The most reliable way to do email validation in JavaScript - is to use an external library that has been proven by hundreds of thousands of other developers.
In some of my projects I have used email-validator, which is very popular, even though is probably no longer maintained (the last release was 3 years ago):
import validator from "email-validator";
validator.validate("johndoe@gmail.com"); // trueYou can visit library's Github page, open the index.js file, and check out what Regular Expression is used under the hood.
There are many other alternatives in the NPM registry, just look for one that meets your requirements.
Pros And Cons Of All Approaches
Each approach has its own pros and cons, which we will point out in this section:
-
Regular Expression
Pros:
- Can be easily adjusted
Cons:
- Difficult to choose appropriate Regular Expression
-
Built-in HTML5 validation
Pros:
- Native implementation
Cons:
- More difficult to customize
- Can be disabled in the Developer's Console
-
Third-party library
Pros:
- Proven to work for hundreds of thousands of developers
- Contains unit tests that check for edge cases
Cons:
- Adds extra KBs to your bundle
- Need to check the license
What Approach Is The Best?
Ultimately, we need to figure out which approach is best.
I would recommend a mix of the second and third approaches - it costs you nothing to add an email type input that uses the built-in HTML5 email validation, and then install and use an external library for even more security.
The disadvantages of using an external library are not really accurate, as these libraries are so small that adding them costs almost nothing (the size of email-validator, according to BundlePhobia is 300B minified + gzipped) and the licence usually allows you to use the library in your commercial projects.
However, remember that validating emails on the server side is by no means less important than validating them on the client-side.
Someone can send a request to your backend from Postman without using your frontend, and you will end up with incorrect data in the database.
Summary
Email validation is a very important topic, understanding it will help you to build better and more secure applications.
In this article, we have learned 3 ways to validate an email address in JavaScript: Using a Regular Expression, built-in HTML5 validation, or a third-party library.
Each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages and it's entirely up to you to decide what to use depending on the circumstances.
Remember that validating emails on the client-side is only one piece of the puzzle - emails need to be validated on the backend as well.