How To Make Your React Application SEO-Friendly?
Table Of Contents
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a process of improving the quality and quantity of website traffic to a website from search engines.
An enormous number of people use Google as a tool to search for information, so it is extremely important that your website is ranked as high as possible in search results.
The higher you rank, the more traffic you receive, as simple as that.
Before we start learning what problems with SEO and React are and how to get rid of them, let's get a really quick overview of how websites are indexed by Google.
Step 1: Crawling
There is no single place where all websites are registered, so Google has to constantly search for new websites and add them to its list.
This process is called crawling.
It uses a lot of Google Bots (web crawlers) to do this kind of work.
Step 2: Indexing
After your website is found, Google Bot tries to understand what it is about by processing the text content, key tags and attributes, images, videos, and more.
This process is called indexing.
The results of indexing are stored in the Google index, an enormously large database.
Step 3: Ranking
Google implements an algorithm that decides which results from its index to display in response to user queries.
There are hundreds of rules that are used to determine relevant results.
Some of these include page load time and mobile-friendliness, so make sure your website loads fast and works well on mobile devices.
Check your website on the PageSpeed Insights to get some important information about what can be improved to rank even better.
To get a deeper understanding of what the whole process looks like, read "How Google Search Works" by Google.
How Is JavaScript Processed By Google?
JavaScript is used in almost every application nowadays as it gives us many great features to create better, faster and more powerful websites.
Websites built with JavaScript can be rendered on a client or on a server, and the rendering type defines how easy it would be for Google Bots to crawl your website.
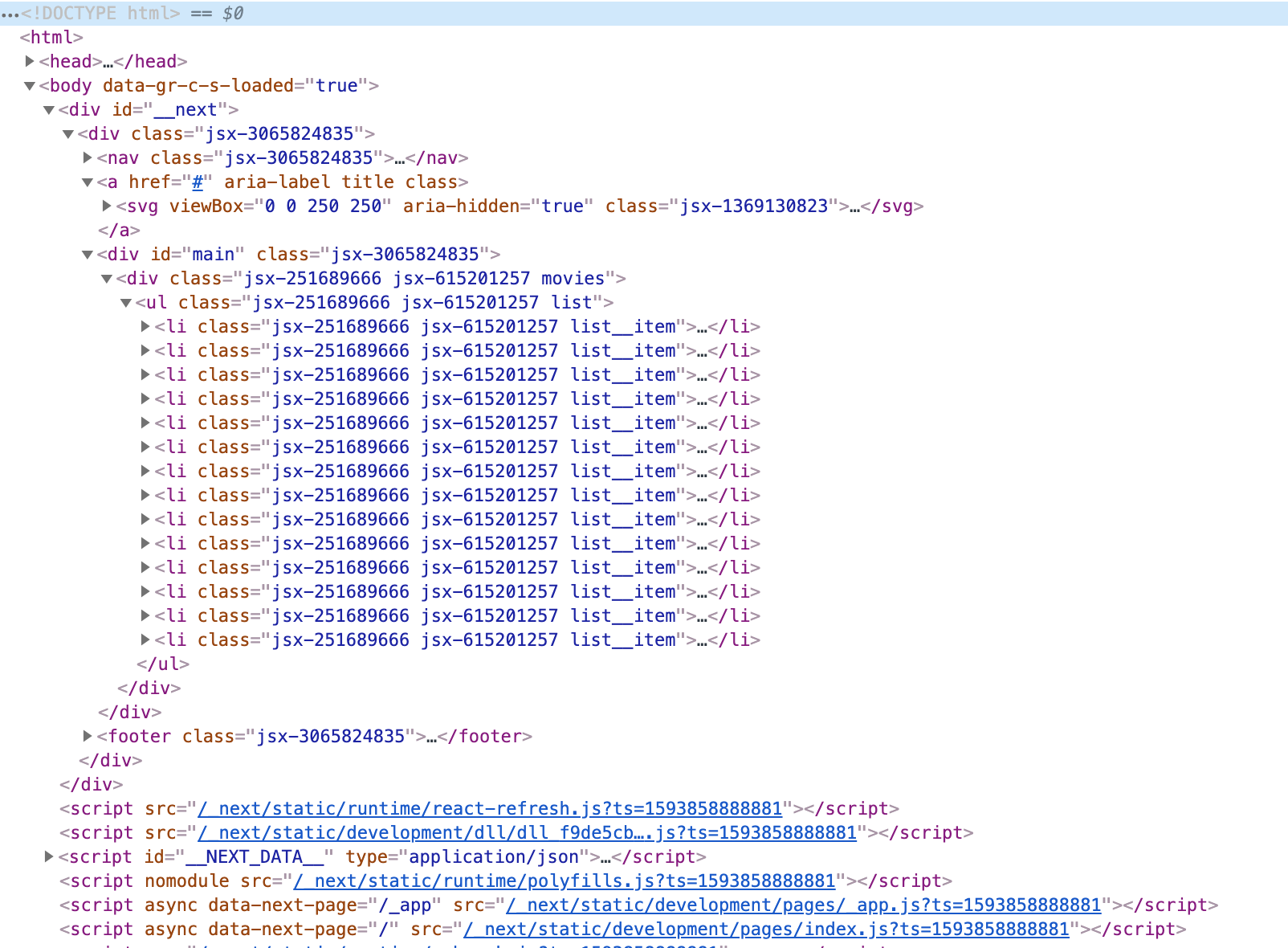
Server-Rendered Applications return HTML with all the content in the HTTP response, while Client-Rendered Applications do not.
HTTP response of a Server-Rendered Application:
HTTP response of a Client-Rendered application:
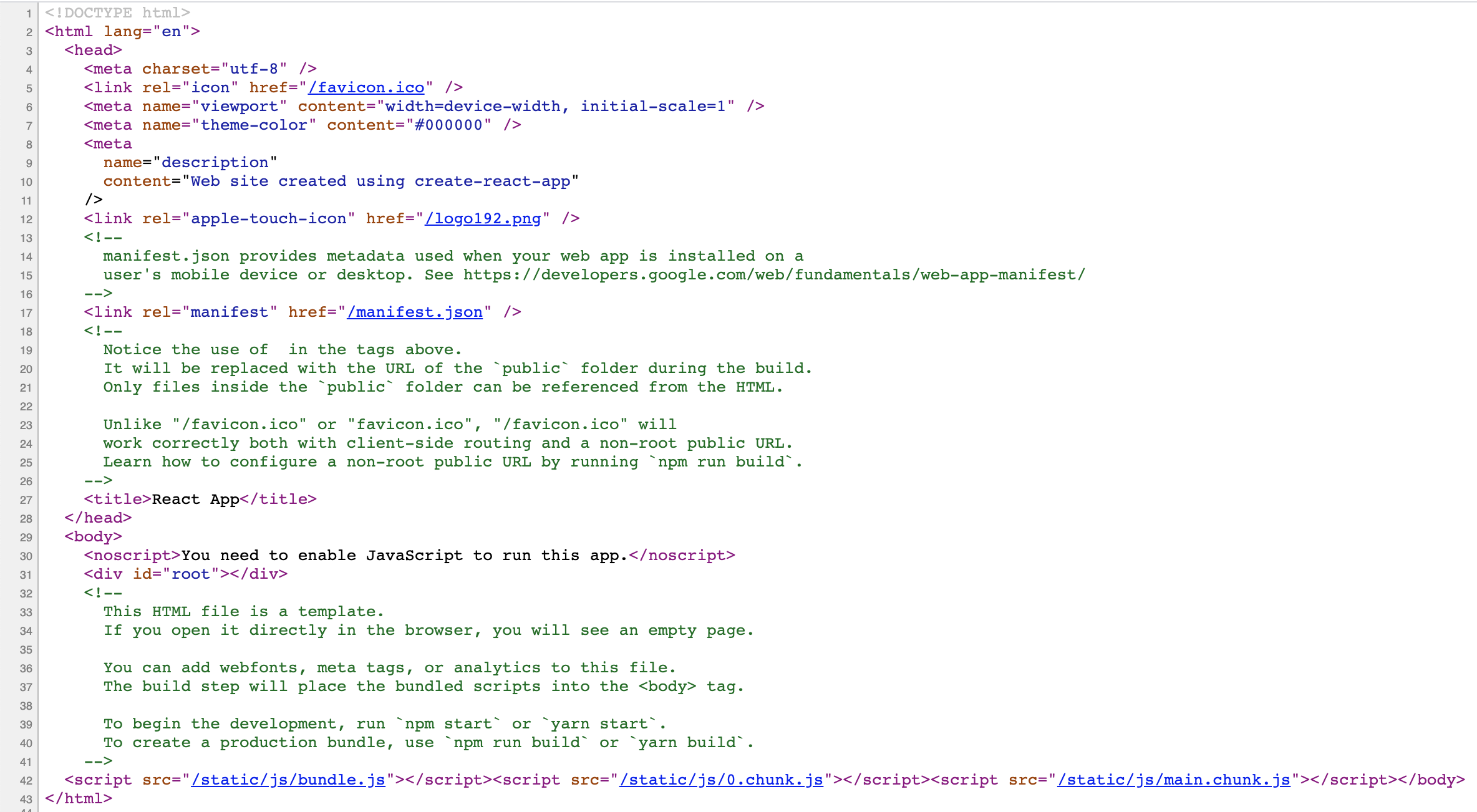
Important note: Notice, that <div id="root"></div> element is empty. After executing JavaScript files, the entire React application will be rendered in it unless you change that.
If no full HTML is returned, Google Bots will run JavaScript and wait for completion to see the website data, which will then be indexed and saved.
This process is complicated and there are many things that can go wrong, so it's a bit risky to rely on it.
In summary, while your Client-Side JavaScript application can be indexed, it is still better to use Server-Side or Pre-Rendering as it will make your website faster for both users and crawlers.
Common JavaScript Issues
The most common issues with JavaScript:
- If it contains an error, a Google Bot will see a blank page and index it
- If it takes too long to load, your crawl budget will be drained by the smaller number of pages, so some pages would not be indexed
Crawl budget is the level of attention Search Engine pays to your website.
If it is wasted, fewer pages will be indexed.
If you have Google Search Console connected to your website, go to Settings -> Crawl Stats and see how many of your pages are crawled daily.
This report can be used to detect whether Google encounters serving problems when crawling your site:
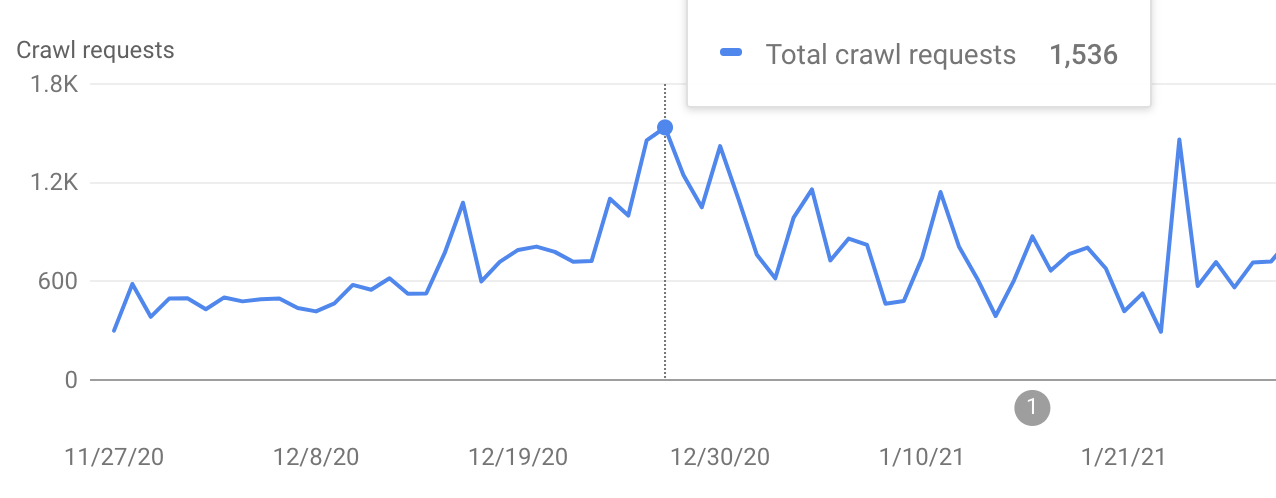
The higher the response time, the lower the number of crawl requests would be.
Tip 1: Use Pre-Rendering
Pre-Rendering is a process of pre-loading website content using the Headless Chrome to prepare it for web crawlers.
Headless Chrome is a way to run the Chrome browser in a headless environment. Essentially, running Chrome without chrome! It brings all modern web platform features provided by Chromium and the Blink rendering engine to the command line.
Typically Pre-Rendering is done with the help of a service (like prerender.io) or library (like react-snap) that intercepts all requests to your website and checks the user-agent to determine if a website is being requested by a robot or a human.
If a viewer is a bot, it gets Pre-Rendered version of a website (cached HTML).
If a viewer is a human, a website loads normally.
Pros Of Pre-Rendering
- Allows Google to see the content for indexing
- Easy-to-implement (compared to Server-Side Rendering or Isomorphic Applications)
- Lighter server payload (compared to Server-Side Rendering)
Cons Of Pre-Rendering
- Most services that can be used for Pre-Rendering are paid and work poorly with dynamic content
Tip 2: Use Server-Side Rendering
With the Server-Side Rendering (SSR) approach, HTML code is generated on the server.
Whenever a website is visited, the browser makes a request to the server, which generates and returns the HTML content.
There is a great open-source framework called Next.js that enables SSR for React-based web applications.
It relieves many of the problems developers typically face when trying to set up SSR from scratch, is easy to start, and has great documentation.
Consider using it if you are building a website that requires good SEO.
Pros Of SSR
- Good for frequently-updated websites
- Fast initial loading
Const Of SSR
- High server load
Tip 3: Use Static-Site Generator
Static-Site Generation is a process of generating pages at the build time to make them available immediately upon user request.
The biggest difference with the "traditional" approach (like SSR or Client-Side Rendering) is that Static-Site Generator does this in advance for each page you deploy, rather than waiting for the page to be requested and generated on-demand.
One of the biggest advantages is speed, and Search Engines really like that.
Statis-Site Generator is a tool that takes your templates, fills them with content, and spits out HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
One of the most popular open-source Static-Site Generators is GatsbyJS.
It uses React in conjunction with GraphQL, has great documentation and lots of useful plugins that make development super fun.
Pros Of SSG
- Performance
- Flexibility
- Low server load
Cons Of SSG
- Difficult to manage frequently-updated content - the website needs to be rebuilt to generate newly added pages
- Long build time
Tip 4: Build Isomorphic Application
Isomorphic (Universal) Application - is an application that can run on both the server and the client.
In an Isomorphic Application, the first request is processed by the server and subsequent requests are processed by the browser.
This approach allows web crawlers to get the full HTML code in their request and index the web page.
Pros Of Isomorphic Apps
- Full SEO support
- Fast initial loading
- Fast processing of subsequent requests on the client-side
Cons Of Isomorphic Apps
- Difficult configuration
Summary
There are a few ways to make your React application SEO-Friendly: Pre-Rendering, Server-Side Rendering, Statis-Site Generation, Isomorphic Application.
There is no "recommended" approach, each one comes with their own costs.
To choose the right path, you need to know exactly what kind of application you are building and how many resources are available.