Algorithms | Selection Sort in JavaScript
Table Of Contents
In this article, we will learn Selection Sort - a simple and easy-to-implement comparison algorithm, which serves as a basis for some of the most widely-used sorting algorithms, such as Heap Sort.
It is often used for educational purposes due to its simplicity.
Selection Sort has retained its name because it repeatedly selects the next-smallest element and swaps it into the right place.
The Definition
Selection Sort is a simple and easy-to-implement comparison algorithm.
It divides the input array into two sublists - a sorted one, which is built up from left to right and a sublist of the remaining unsorted items, which take up the rest of the list.
First, the sorted sublist is empty and the unsorted sublist contains the entire input array.
An algorithm works by finding the smallest (or the largest, depending on the order) element in the unsorted sublist and swapping it with the leftmost unsorted element, thereby extending the length of the sorted sublist.
This process continues until the entire input array is sorted:
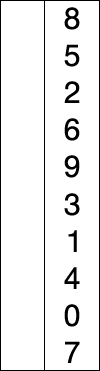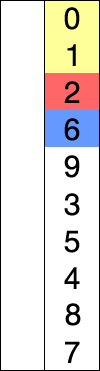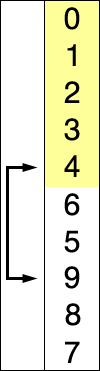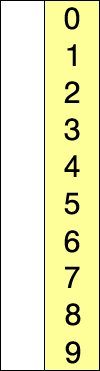
The visualization:

The Complexity
Selection Sort has a rather poor average time complexity because it takes two loops to complete itself.
Best-case performance - O(N^2).
Worst-case performance - O(N^2).
Average - O(N^2).
Pros And Cons
Even though the algorithm is inefficient, it was a base for some widely used sorting algorithms, like Heap Sort.
Pros
- Simple implementation
- Performs well on small arrays
- Has performance advantages over the other sorting algorithms in specific situations, for example when auxiliary memory is limited
Cons
- Inefficient, especially for large datasets
Implementation In JavaScript
const selectionSort = (arr) => {
// Get the length of the input array
const length = arr.length;
// Iterate over all elements
for(let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// Assume that the first element is the smallest
let min = i;
// Iterate over the rest of the array
for(let j = i + 1; j < length; j++) {
// If current element is smaller than the smallest one
// Assume it is the smallest one
if(arr[j] < arr[min]) {
min = j;
}
}
// If the smallest element is not the first one
if(min !== i) {
// Swap the smallest element with the current one
[arr[i], arr[min]] = [arr[min], arr[i]];
}
}
// Return sorted array
return arr;
}Usage In JavaScript
// Assuming that the selectionSort function from the example above is accessible
const arr = [15, 4, 8, 9, 1, 11, 2];
console.log(selectionSort(arr)); // Prints "[1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 11, 15]"Summary
In this article we have covered the basics of the Selection Sort algorithm and found that it serves as a basis for some of the most widely used algorithms, such as Heap Sort and itself is not used very often.
If the input array is small, it may be a better choice than Merge or Quick Sort, but not Insertion Sort.
If the input array is large, Selection Sort it is definitely not the right algorithm to continue.