Algorithms | Insertion Sort In JavaScript
Table Of Contents
Today we will learn a very simple algorithm that works best for small or almost sorted records and is not efficient for the larger or unsorted ones.
It works on the principle of inserting an element at a certain position, that is why it is called Insertion Sort.
The Definition
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that builds the final sorted array one item at a time.
An algorithm iterates up the array, growing the sorted list behind it.
For each array item, it compares the value to the largest element in the sorted list (which happens to be the previous element).
If it is larger, we leave the element on its current position and move to the next one.
If it is smaller, we find the correct position for this element in the sorted list, shift all larger values up to make space and insert it.
The resulting array after k iterations has k + 1 sorted elements (+ 1 because the first element is skipped):
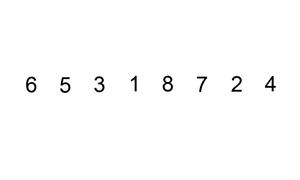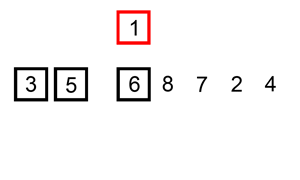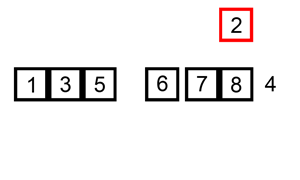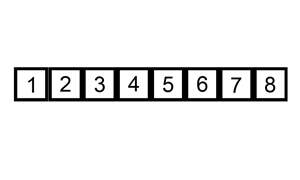
The visualization:
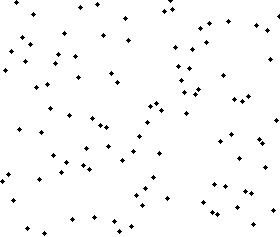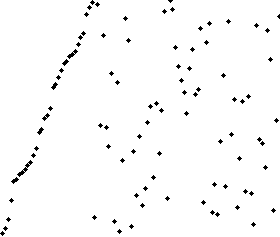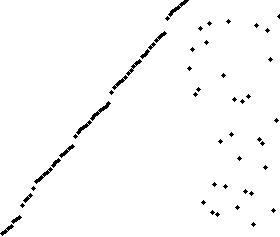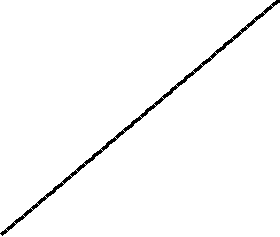
The Complexity
Best-case performance - O(N), if the input array is already sorted.
Worst-case performance - O(N2), if the input array in the decreasing order.
Average - O(N2).
Pros And Cons
Insertion Sort has a fast best-case running time and is a good sorting algorithm when the input list is already mostly sorted.
For larger or more disordered lists, an algorithm with a faster worst and average-case running time, such as Merge Sort, would be the better choice.
Pros
- Simple implementation
- Efficient for small data sets
- Efficient if the input array is almost sorted
-
Stable sort
Does not change the relative order of elements with equal keys.
-
Memory efficient
Only requires a constant amount
O(1)of additional memory space.
Cons
- Inefficient for large data sets
Implementation In JavaScript
const insertionSort = (arr) => {
// For each element in an array
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// Get the current element
const current = arr[i];
// Get the index of the previous element
let j = i - 1;
// We skip the first element, as it is considered sorted
// While current element is smaller than the previous
while(j >= 0 && current < arr[j]) {
// Shift element to the right
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
// Go to the previous index
j--;
}
// We found the position, insert the current element
arr[j + 1] = current;
}
// Return sorted array
return arr;
}Usage In JavaScript
// Assuming that the insertionSort function from the example above is accessible
const arr = [1, 56, 32, 12, 13, 11, 9];
console.log(insertionSort(arr)); // Prints "[1, 9, 11, 12, 13, 32, 56]"Summary
Insertion Sort is a very simple algorithm that works best for small or almost sorted records. For large data sets, Merge or Quick Sort is a better choice.